Cory:
Unlock Your AI Assistant Now!

In this issue of EuroIntervention, Heshmatollah et al from the MR CLEAN (Multicenter Randomized CLinical trial of Endovascular treatment for Acute ischemic stroke in the Netherlands) Study Group present secondary analysis1 from their landmark randomised trial2.
I was surprised at how the authors set out their aims, “The aim of the present study is to determine if atrial fibrillation (AF) modifies the effect of endovascular treatment”. I do not agree with the way in which the aims were formulated and I will try to explain why.
The observations that patients with acute ongoing cerebral ischaemia caused by cardioembolic occlusions tend to have worse outcomes after any (not only endovascular!) treatment than patients with ischaemic stroke of other aetiologies are known3. However, this cannot be interpreted as meaning that atrial fibrillation itself modifies the effect of endovascular treatment. Such a statement could lead to dangerous conclusions, e.g., to scepticism, leading to denying endovascular treatment to patients with atrial fibrillation.
The fact that outcomes of patients with atrial fibrillation and acute ischaemic stroke are inferior to patients with stroke without AF can be explained simply by the fact that AF presence is a marker of more serious cardiovascular disease4. The large (mean 12 years!!) age difference may simply explain the results of this study – obviously older patients (with AF) have inferior outcomes when compared to a substantially younger group (without AF). Furthermore, patients with AF in this study had longer time delays. We may expect that cerebral ischaemia caused by a sudden embolus from the heart (coming to an “unprepared brain“) can progress faster than ischaemia caused by, e.g., progressive carotid stenosis (where there may be time for development of collaterals). This is well known from coronary artery disease: patients suffering ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) as the first symptom of their disease have a larger infarct size compared to patients with STEMI after some period of angina pectoris. Thus, AF-related cerebral ischaemia may be progressing faster, but in the MR CLEAN study it was treated later compared to patients without AF. It is thus not surprising that outcomes are inferior compared to stroke without AF.
Our experience supports these comments: our patients with AF are older, more obese, more frequently have renal failure and less frequently have visible collaterals (Table 1).
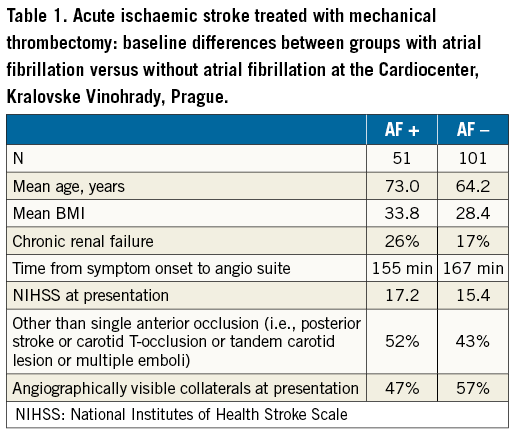
Furthermore, it is known that thrombolysis is less used in patients with AF-related stroke and, if used, has only limited effect. Thus, it is dangerous to present sceptical comments about the effect of mechanical thrombectomy in AF, when in fact such treatment might be the best chance for these patients. The most important question for future research might be whether the time window for indication of thrombectomy might be shorter in AF patients than in patients without AF. Of course, this apparently logical presumption would require a dedicated study.
Conflict of interest statement
The author has no conflicts of interest to declare.

